After experiencing a stroke, survivors often experience physical problems with co-ordination and balance as well as cognitive problems such as difficulties with vision and attention.
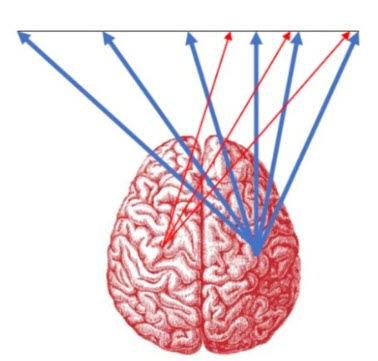
You may have difficulty processing visual information after a stroke and/or struggle to make sense of this information. Often it’s possible to struggle with something called ‘spatial inattention’ which affects your perception of one side of your visual field. Even if you have good eyesight, your brain doesn’t process the information that it’s getting from one side. A left hemisphere stroke for example, could cause you to lose awareness of things to the right side of your body.
Additionally, it’s common to experience attentional problems after a stroke, where you might find long periods of concentration and tasks consisting of multiple pieces of information much more difficult.
These vision and attentional problems are often known as ‘spatial neglect’ and the estimated prevalence after unilateral stroke is 30%, with the incidence incidence across studies varying from 12% to 90%. Data shows that in the UK post-stroke, patients suffering with spatial neglect have an increased length of hospitalisation of 27 days compared to 10 days for patients without spatial neglect. Neglect often prevents patients’ level of participation within rehabilitation and so new ways of engagement in rehabilitation are being explored.
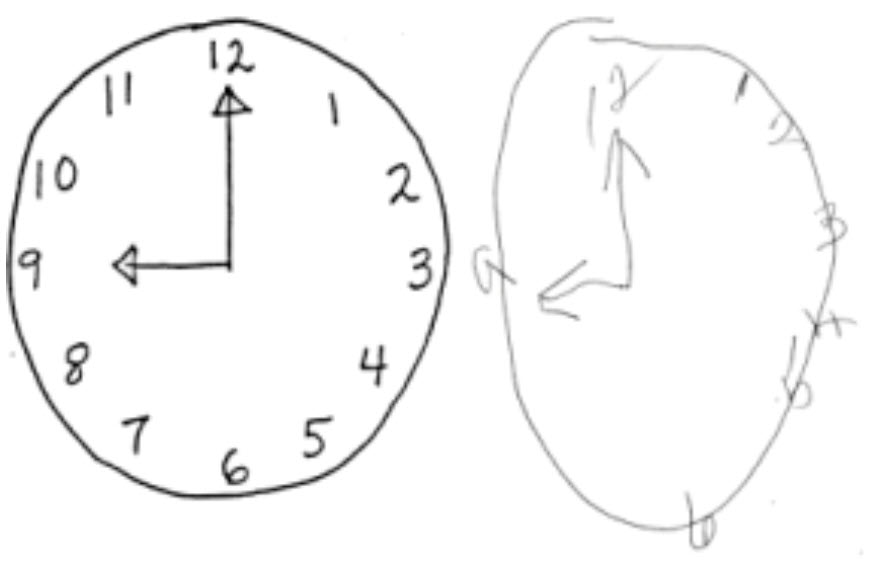
Here is a clock face showing a patient’s copy to the right. Not uncommonly, patients with left neglect might sketch a clock by drawing the entire circle and writing the numerals 12, 3, 6, and 9 at their correct locations, omitting those on one side but being satisfied that the entire clock face had been sketched. In this example, note the bunching of numerals on the right side, another characteristic of clock drawing by patients with neglect.

A simple retraining method to help increase survivors’ awareness of the neglected side is for the therapist or trainer to encourage you to try to describe items in the more-affected visual field space. Another method commonly used clinically, in community care as well as an at home resource is to encourage the use of dedicated apps.
Apps are posited to help with healthcare costs, help enhance at home rehabilitation, increase engagement (in and out of hospital) and can ensure accurate monitoring of the patient from healthcare professionals.

However, what is less known is: which apps stroke patients, carers and healthcare professionals utilise the most and their opinions about them.

For this reason, researchers at the Neuropsychology Laboratory at the University of East Anglia (at which Dr Balchin is an Honorary Senior Research Fellow), have asked ARNI to help with research, which is funded by the Stroke Association.
The University is inviting stroke survivors, care givers and clinicians to participate in a survey, which explores whether (and how) apps are used to rehabilitate vision and attentional difficulties following stroke. The survey aims to understand real opinions of these apps in order to better inform practise and development.

Would you like to help? We need you to take part: please do!
If you would like to, the online survey will take you just 15 minutes to complete.
- If you are a Stroke Survivor, click here: https://ueapsych.eu.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_eQDHVQVWRom1c9g
- If you are a Family Member/Carer, click here: https://ueapsych.eu.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_3soJR4uKV2a1vZI
- If you are a Healthcare Professional, click here: https://ueapsych.eu.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_0ixwGweIIuxUmJU
All survey responses are anonymous.

 The survey is supervised by Dr Stephanie Rossit and has been granted ethical approval by the School of Psychology Ethics Committee at the University of East Anglia.
The survey is supervised by Dr Stephanie Rossit and has been granted ethical approval by the School of Psychology Ethics Committee at the University of East Anglia.
If you have any further questions, please do not hesitate to get in touch via email to ARNI or straight to neurolab@uea.ac.uk.
Checketts, M., Mancuso, M., Fordell, H., Chen, P., Hreha, K., Eskes, G. A., Vuilleumier, P., Vail, A., & Bowen, A. (2020). Current clinical practice in the screening and diagnosis of spatial neglect post-stroke: Findings from a multidisciplinary international survey. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 1–32.
Halligan, P. W., & Robertson, I. (1999). Spatial neglect: A clinical handbook for diagnosis and treatment. Psychology Press.
Esposito, E., Shekhtman, G., Chen, P. (2021) Prevalence of spatial neglect post-stroke: A systematic review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 64(5), 101459.




2 Comments
vmaxgdqupvlwzabnjhhmkjpscmmefd
Can you help me with loss of vision please